 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
|
 Section
IV.
TROUBLESHOOTING
3-6. G e n e r a l
corrective actions given in this chart do not correct
the
malfunction,
report
the
trouble to
This section describes troubles which might occur
organizational maintenance.
during operation of the reciprocating pump, along
with the probable causes and corrective actions
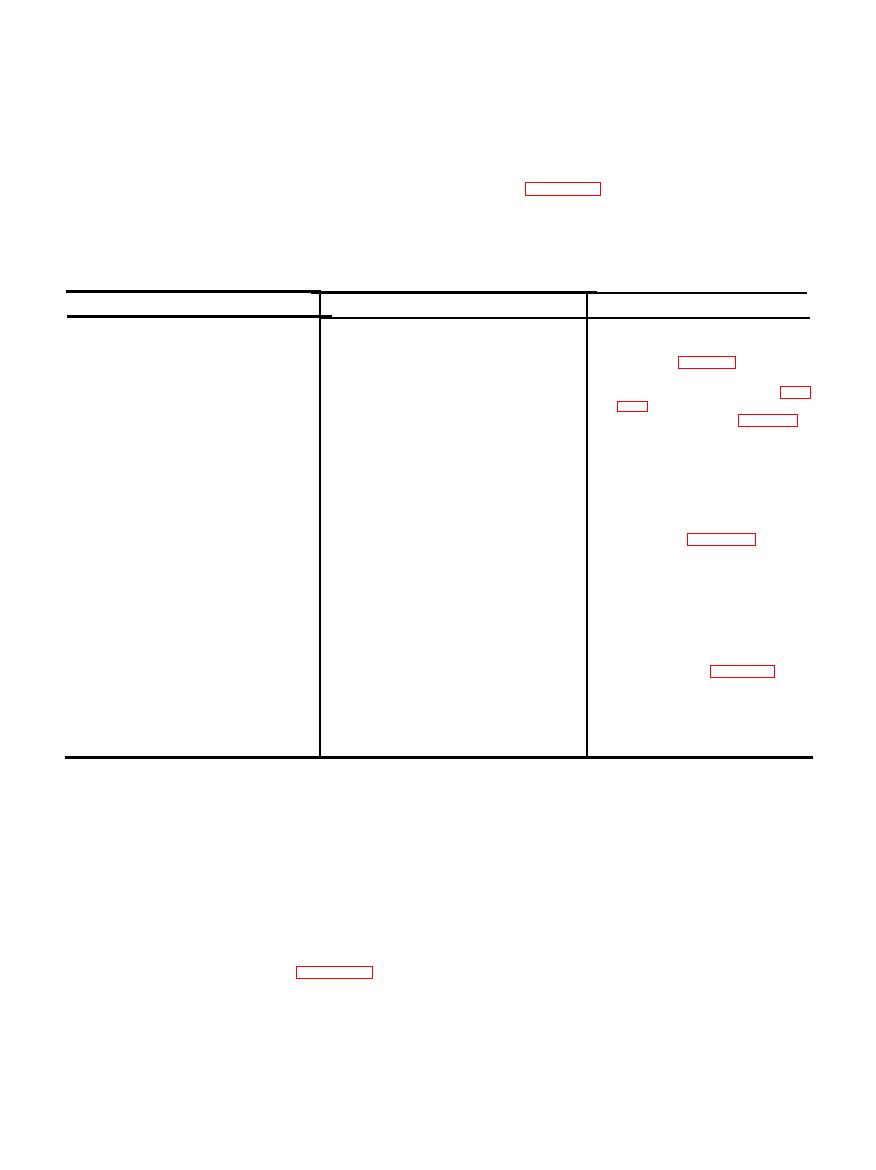
3-7. Operator / Crew Troubleshooting Chart
relating to the troubles. Only those malfunctions
Refer to table 3-2 for troubleshooting which is
which are within the maintenance scope of the
a l l o c a t e d to the operator/ crew level of main-
operator / crew are included in this chart. If the
tenance.
Probable cause
Malfunction
Corrective
action
1. Engine turns over but fails to
a. Fill fuel tank.
a. Fuel tank empty.
fuel
tank.
b. Drain
Service
b. Water in fuel.
start.
fuel strainer para 3-9). Refill tank
with fresh, uncontaminated fuel.
c. Ignition switch in OFF position
2. Engine starts but then stops.
a. Fuel filter clogged.
b. Fill fuel tank.
b. Insufficient fuel supply.
a. Clean hose or suction strainer.
a. Suction hose or strainer clogged.
3. Engine starts but pump fails to
b. Suction leak.
pump.
b. Tighten all suction connections.
c. Suction strainer and hose not fully
c. Submerge suction strainer and
submerged.
hose.
d. Suction lift too high.
d. Reduce suction lift to less than 25
feet.
e. Pump not primed (suction lifts 15
e. Prime pump (para 2-10c).
to 25 feet).
f. Foreign material lodged under
f. Remove foreign material from
valve.
valve.
g. Static discharge head too high.
g. Lower discharge bead.
4. Pump output to low.
a. Suction hose or strainer clogged.
a. Clean suction hose or strainer.
b. Suction leak.
b. Tighten all suction connections.
c. Throttle lever not in full-speed
lever so
c. O p e r a t e
throttle
t h a t engine operates at full
position.
governed speed (fig. 2-2).
d. Use 4-inch discharge hose.
d. Diameter of discharge hose too
small.
e. Remove foreign material from
e. Foreign material lodged under
valve.
valve.
f. High static discharge head.
f. Lower discharge head.
Section V. MAINTENANCE OF FUEL STRAINER
release the fuel bowl (3). Remove the fuel bowl and
3-8. General
gasket. Empty the contents of the fuel bowl and
The fuel strainer is installed in the fuel system
wipe it clean with a lint-free cloth.
between the fuel tank and the engine carburetor. It
c. If necessary, remove the fuel filter element (4)
f i l t e r s dirt, sand, and moisture from the fuel,
and clean it with an approved cleaning solvent.
preventing these foreign materials from disrupting
Shake out excess solvent.
the operation of the carburetor.
d. Reassemble the fuel strainer parts and tighten
3-9. Fuel Strainer Service
the bail nut to position the fuel bowl
e. Open the fuel shutoff valve and check for
b. Loosen bail nut (5) and swing the bail (6) to
leaks. Correct any leaks.
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |