|
| |
TM 5-4320-305-10
1-13.
PUMPING OPERATION
After the pump body is primed and pumping begins, liquid is pumped through the pumping components in the following
sequence of operation.
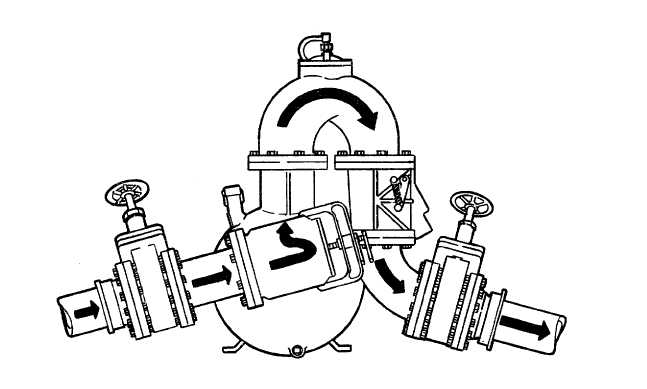
1.
Liquid in the supply hose enters the suction gate valve. If the gate valve is open, the liquid passes through
the valve and enters the suction strainer.
2.
As the liquid passes through the suction strainer, the strainer filters out large particles of debris.
3.
From the strainer, the liquid enters the pump housing through the suction port. The impeller, rotating at high
speed, forces the liquid at the suction port out of the pump body through the discharge port.
4.
The liquid is forced out of the pump body into the discharge elbow, past the air valve, and into the check
valve assembly. If air is in the liquid, the air valve vents it from the discharge elbow.
5.
The discharge check valve permits the liquid to flow from the pump toward the discharge hose, and prevents
it from flowing in reverse through the pump back to the storage container.
6.
Liquid from the discharge check valve enters the discharge gate valve. The liquid passes through the open
valve and enters the discharge hose.
7.
As the sequence 1 through 6 continues, liquid is transferred from the supply through the pumping
components, into the discharge hose.
1-14.
PUMPING BALANCE
The suction and discharge gate valves can be used to limit and/or balance the amount of liquid being pumped in or out of
the assembly. The gate valves can also be used to keep liquid in or out of the system when pumping action stops.
1-12
|